
On May 21, 2024, the 27 EU member states adopted the AI Act, a comprehensive framework for regulating Artificial Intelligence (AI) within the European Union. This regulation is the world’s first comprehensive legal framework for AI, aiming to establish uniform standards and guidelines for the deployment of AI technologies. With the AI Act, the EU has laid a strong foundation for the regulation of artificial intelligence, promoting both trust and acceptance of the technology, as well as enabling innovations “made in Europe.”
The adoption of the AI Act by the EU Council is a significant step that will shape the future of artificial intelligence in Europe. The AI Act aims to maximize the benefits of AI while minimizing the risks. Through clear regulations and stringent requirements, it ensures that AI systems are deployed safely, transparently, and ethically. A crucial aspect of deploying AI ethically involves sentiment detection, which can help in understanding and navigating the intricacies of human emotions in digital communications.
In this blog post, we present the background and key contents of the AI Act, the specific provisions and their impact on innovation and the economy. We also highlight the national implementation in the member states and the international perspective of the AI Act.
Key Takeaways
- On May 21, 2024, the EU adopted the AI Act, creating the world’s first comprehensive legal framework for AI regulation.
- The AI Act categorizes AI applications by risk levels (unacceptable, high, limited, minimal) and applies specific measures to ensure safety and transparency.
- Certain AI applications, such as social scoring by authorities and mass biometric surveillance in public spaces, are banned under the AI Act.
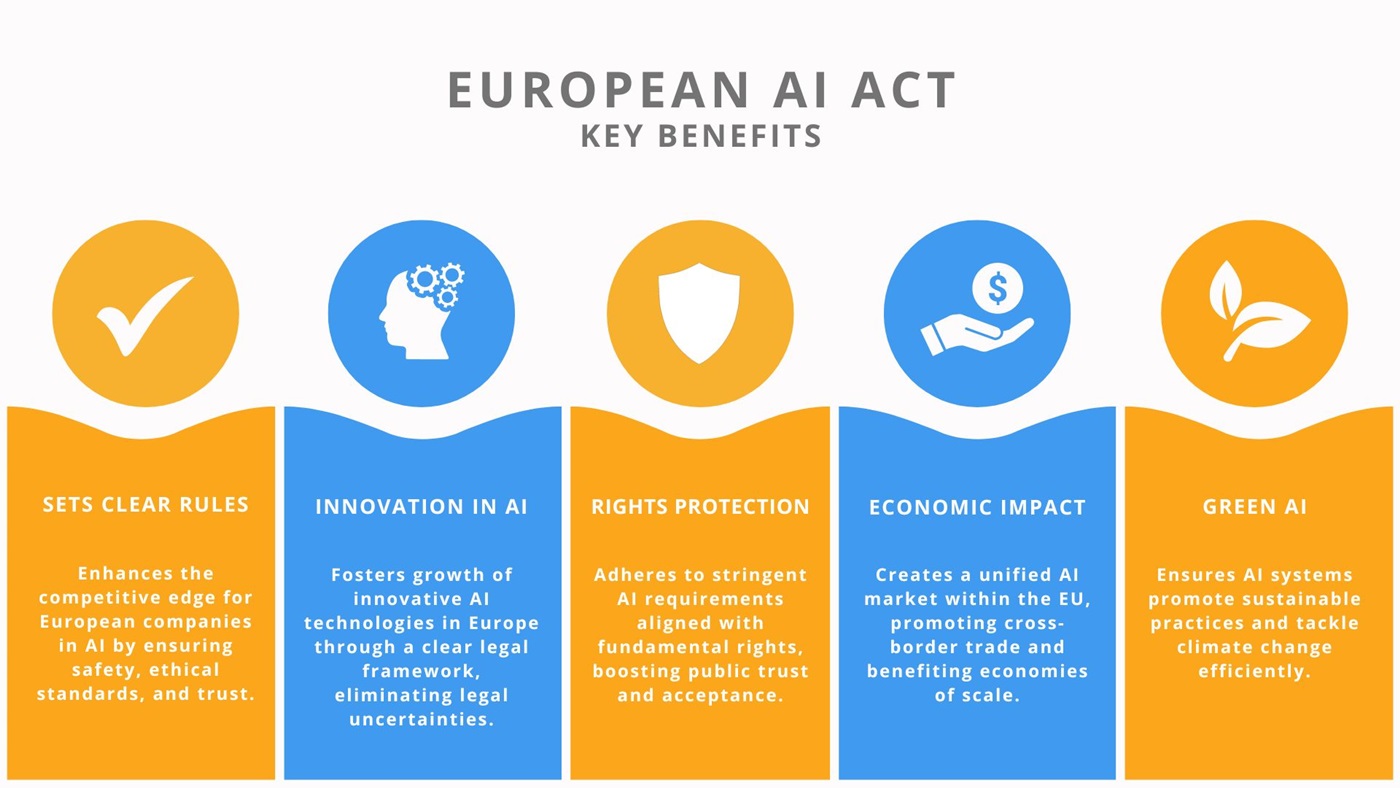
- By creating a stable regulatory environment, the AI Act promotes innovation and ethical AI use, giving European companies a competitive advantage.
- The AI Act sets new international standards for AI regulation, potentially influencing similar regulatory frameworks in other regions.
The regulation of artificial intelligence in the European Union has a long history. As early as the 2010s, the EU began to address the challenges and opportunities of AI intensively. Early initiatives aimed to develop ethical guidelines for the use of AI and to adapt the legal framework. However, with the increasing proliferation of AI technologies, it became clear that more comprehensive and binding regulations were necessary.
In April 2021, the European Commission finally presented a proposal for the AI Act. This was based on a risk-based approach that defines various levels of AI risks and proposes corresponding measures. The proposal was intensively discussed and revised several times before it was adopted by the EU Council in May 2024.
In a global comparison, the EU takes a pioneering role with the AI Act. While other countries, such as the USA and China, are also working on regulatory approaches, the AI Act is the first comprehensive legal framework of its kind. It focuses not only on strict safety and transparency requirements but also on promoting innovation and protecting fundamental rights.
The adoption of the AI Act is a milestone in the development of AI regulation and shows that the EU is ready to take a leading role in shaping the digital future. By setting clear rules and guidelines for the use of AI, the EU creates trust and acceptance for this technology while promoting its responsible and ethical use.
In the next sections, we will examine the specific contents and regulations of the AI Act in more detail and analyze their impact on the European economy and society.
The AI Act is a comprehensive regulation that addresses various aspects of artificial intelligence. The central contents of the Act include:
The AI Act thus adopts a balanced approach that ensures both the protection of citizens and the promotion of innovation in the field of artificial intelligence in Europe. By implementing clear regulations and high safety standards, the trust in AI technologies is strengthened, and their ethical use is promoted.
The AI Act contains specific provisions regulating the use of artificial intelligence:
These regulations aim to strengthen trust in AI technologies while ensuring their responsible and ethical use. The Act thus creates a clear framework that ensures both the protection of citizens and the promotion of innovation.
The AI Act has far-reaching implications for innovation and the economy in Europe. On one hand, it imposes stringent requirements and safety standards for AI systems, which may initially seem like a hurdle for businesses. On the other hand, by providing clear and uniform regulations, it creates a stable and predictable environment that fosters investment and innovation.
Overall, the AI Act lays the foundation for a dynamic and secure innovation environment in Europe. By combining stringent safety requirements with the promotion of innovation, the regulation enhances the competitiveness of European companies while also contributing to the protection of fundamental rights.
The implementation of the AI Act in the individual member states of the European Union poses a significant challenge but also requires close cooperation and coordination. Each member state is responsible for transposing the provisions of the AI Act into national law and creating appropriate enforcement mechanisms.
National governments must establish their own supervisory authorities or adequately equip existing institutions to monitor compliance with the AI Act’s requirements. These authorities are responsible for conducting inspections, evaluating AI systems, and imposing sanctions for violations.
Implementing the AI Act requires substantial adjustments in national legal systems and administrative structures. In particular, technical expertise and resources must be built up to meet the complex requirements of the regulation. Additionally, there is the challenge of ensuring uniform standards across all member states and minimizing differences in implementation.
Germany, as one of Europe’s technologically leading countries, has the chance to take a pioneering role in the national implementation of the AI Act. By developing and implementing stringent and innovative regulations, Germany can set standards both nationally and internationally and strengthen its position as a technology leader.
Leading politicians and institutions have emphasized the importance of the national implementation of the AI Act. They highlight the need to ensure both the protection of citizens’ rights and the promotion of innovation. Statements from political actors underline the willingness to actively address the challenges of implementation and seize the opportunities arising from the regulation.
Overall, the national implementation of the Act requires close cooperation between the member states and the EU to effectively achieve the regulation’s goals. By creating uniform standards and promoting innovation, Europe can further strengthen its position as a leading region for ethical and safe AI technologies.
The AI Act has attracted attention not only within Europe but also globally. As the first comprehensive framework for regulating artificial intelligence, the EU is setting new standards that are being noticed beyond its borders.
International organizations such as the United Nations and the OECD have recognized the AI Act as groundbreaking. They praise the risk-based approach and the comprehensive protection mechanisms that underlie the regulation.
Global technology companies have responded to the AI Act with mixed feelings. While some welcome the clear regulations and ethical focus, others view the stringent requirements as potential obstacles to innovation and market entry.
The AI Act could serve as a model for future AI regulations in other countries and regions. Countries like the USA and China are closely monitoring developments in Europe and may adopt similar regulations or introduce their own initiatives for AI regulation.
The AI Act promotes both international cooperation and competition in the field of artificial intelligence. By establishing high standards, Europe could strengthen its position as a leader in the safe and ethical use of AI, while encouraging other regions to adopt comparable measures.
The AI Act helps create global awareness of the need for responsible and regulated AI usage. This could lead to a harmonized international approach to AI regulation, promoting technological advancement while protecting people’s rights and safety worldwide.
Overall, the AI Act has the potential to influence far beyond Europe’s borders. By setting high standards for the use of artificial intelligence, the EU is making a significant contribution to the global discussion on the ethical and safe use of this groundbreaking technology.
The AI Act represents a significant advancement in the regulation of artificial intelligence in Europe. As the world’s first comprehensive framework, it establishes high standards for the safety, transparency, and ethics of AI technologies. The EU creates a reliable and trustworthy environment that ensures both the protection of citizens’ rights and the promotion of innovation.
With clear and uniform regulations, the AI Act provides European companies with the opportunity to position themselves as leaders in the safe and ethical use of AI. This strengthens Europe’s competitiveness in the global market. The national implementation of the AI Act poses challenges but also presents the chance to assume a leading role in the international technology landscape.
Internationally, the AI Act serves as a model and could lay the foundation for similar regulations in other parts of the world. The EU demonstrates its readiness to take a leading role in the global discussion on the future of artificial intelligence.
Overall, the AI Act is not only a milestone for Europe but also has the potential to influence the global development and use of artificial intelligence sustainably. Europe has taken an important step to maximize the benefits of AI while minimizing its risks, thereby contributing to the creation of a safe and innovative digital future.